The world had barely begun to absorb the transformative impact of the 1st Industrial Revolution when, in the late 19th century, a second wave of industrialization swept across the globe. The 2nd Industrial Revolution, also known as the Technological Revolution or the Age of Innovation, brought about a staggering array of technological advancements and social changes that would shape the modern world.
In this blog post, we will explore the key developments, remarkable innovators, and lasting effects of this extraordinary period.
Electricity and the Pioneers of Power

One of the biggest features of the Second Industrial Revolution was electricity. This shift from steam power to electric power brought about a revolution in industry, transportation, and communication. Thomas Edison, often called the “Wizard of Menlo Park,” was a key figure in the development of electricity. He invented the practical incandescent light bulb and created the first electrical distribution system, providing a reliable source of electric power to homes and businesses. Edison’s pioneering work extended beyond the light bulb; he also developed the phonograph and motion pictures, contributing to entertainment and communication. Then there was also Nicola Tesla that was in direct competition with Edison, but that is a very interesting conversation for another time.
Telecommunications and the Birth of Mass Communication
The Second Industrial Revolution also witnessed the birth of mass communication, made possible by advancements in telecommunications. Alexander Graham Bell is renowned for inventing the telephone in 1876, enabling people to communicate across great distances. The telephone revolutionized business and personal communication, connecting individuals and organizations in ways previously unimaginable. At the same time, Guglielmo Marconi made groundbreaking strides in wireless telegraphy. His work laid the foundation for the eventual development of radio communication, a technology that would revolutionize the way information was transmitted and received. Marconi’s experiments with wireless communication led to the first transatlantic radio transmission, marking a significant leap in global communication. And just like with the electricity battle we also saw some big players battle it out over telecommunication, one of these battles even went the legal direction.

The Automobile Revolution
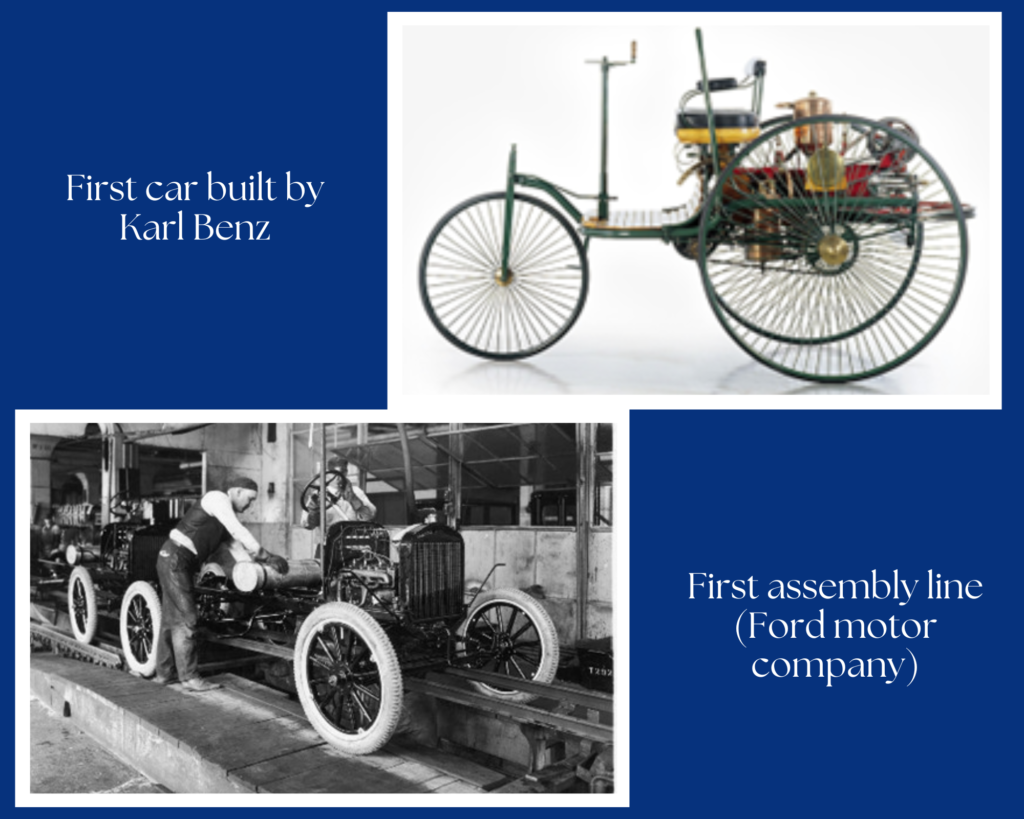
The invention of the car was another hallmark of the Second Industrial Revolution. Karl Benz, a German engineer, is credited with creating the first gasoline-powered car in 1885. His invention paved the way for the automobile industry’s explosive growth, leading to the development of faster, more affordable, and more accessible vehicles. The automobile not only transformed transportation but also impacted society and urban planning, giving rise to suburbs and a more interconnected world because now you could drive to work. Henry Ford, an American entrepreneur, revolutionized automobile production with the introduction of the assembly line in 1913. This innovation dramatically reduced production time and costs, making cars affordable for the masses and transforming the way people travelled. Now everyone could drive to work. Ford’s Model T became an icon of the era, symbolizing mobility and accessibility. Again, there was some fears battles going on in the industry, interesting this also went legal after Dodge decided to also build cars. Note Dodge was a parts supplier for ford at first. But let’s not get sidetracked.
Steel, Skyscrapers, and Urbanization
Steel production and the construction of skyscrapers were instrumental in reshaping urban landscapes during this period. Andrew Carnegie, a Scottish-American industrialist, became a titan of the steel industry, producing huge quantities of high-quality steel. This resource played a crucial role in constructing iconic structures like the Brooklyn Bridge and the Eiffel Tower. Carnegie’s amazing efforts, including funding libraries and educational institutions, left a lasting legacy. The construction of skyscrapers, like the Flatiron Building in New York City, symbolized not only architectural achievement but also the rapid urbanization of the era. Cities grew vertically, accommodating the big numbers of people seeking employment in factories and industries. This transformation laid the groundwork for modern city life and influenced the development of infrastructure and public spaces. This part of the 2nd revolution also led to the world’s first billion-dollar corporation.

The Impact on Labor and Society

Just like in the 1st Industrial revolution. The 2nd Industrial Revolution brought about significant changes in the labour force and social structures. While it generated immense wealth and innovation, it also raised questions about workers’ rights and living conditions. Labor unions gained strength as workers organized to advocate for better wages, shorter working hours, and safer conditions. Unfortunately, the workers of The Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire in 1911, (a tragic event that claimed the lives of 146 workers,) highlighted the urgent need for workplace safety reforms. The labour movement spurred discussions about workers’ rights and led to the implementation of labour laws and regulations. So next time you want to complain about the health and safety at your workplace remember this incident, as it laid the foundation for our safety at the workplace today.
A Legacy of Innovation
The Second Industrial Revolution was a period of unparalleled innovation and transformation. It harnessed the power of electricity, dramatically changed communication, and catapulted the world into the modern age of transportation and urbanization. The impact of this revolution continues to shape our lives today. Electricity and communication as we know it today are the foundations of the modern information age. The automobile remains a cornerstone of personal travel and transportation. The steel and construction techniques developed during this period still influence architecture and engineering in today’s world. Innovations in communication and transportation have connected people across the globe, reshaping how we interact and conduct business.
It reminds us that progress is marked by the ability to adapt and evolve in the face of change. As we navigate the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, the legacy of this era continues to inspire and drive us forward.
As we look back on the innovations of the Second Industrial Revolution, we’re reminded of the incredible power of the human mind.
If you were living back then, which invention or development do you think would have had the biggest impact on your life, and why?
Share your thoughts and travel back in time with us in the comments below!


Hi. Interisting read. Love your work.
Hi Lize,
Thank you for your comment.
We love everything technology, even the history.
Keep your eyes on this space for next months post, it will be a follow up on this one.